Amniocentesis
Amniocentesis is a diagnostic testing that can be done during the pregnancy. Amniocentesis is possible after about 15 weeks of pregnancy. This testing can give you definitive answers about chromosome differences, and other genetic conditions.
Who can have amniocentesis
These are some reasons for having amniocentesis:
- You got a "screen positive" result from enhanced First Trimester Screening (eFTS) or Second Trimester Screening (STS).
- You got a "high risk" result from Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT).
- NIPT failed to give you a result after two tries or more.
- One of your ultrasounds detected a possible problem with the baby. For example, some people choose to have an amniocentesis if there is a large nuchal translucency, or there is a heart defect seen on ultrasound.
- There is a genetic condition running in your family, and you wish to have the baby tested for it before birth.
How to get amniocentesis
If you are interested in amniocentesis, speak to your health-care practitioner about referring you to a specialist in genetics. There, you will get more information about this publicly-funded test, and the team will arrange it if appropriate.
How it works
Amniocentesis is done at specialized centres in Ontario by trained doctors and nurses. An ultrasound is first done to show them where the pregnancy and the placenta are. Using ultrasound as a guide, a thin needle is then inserted through the skin into the fluid around the baby. The needle does not touch the baby. A small amount of fluid is taken and is sent to the lab for testing. The fluid has DNA from the baby and can be tested for genetic conditions.
The procedure generally takes a few minutes. Some people have brief discomfort such as cramping, or pressure during the procedure. You can rest for the day, and you will likely be able to go back to your regular activities within one to two days.
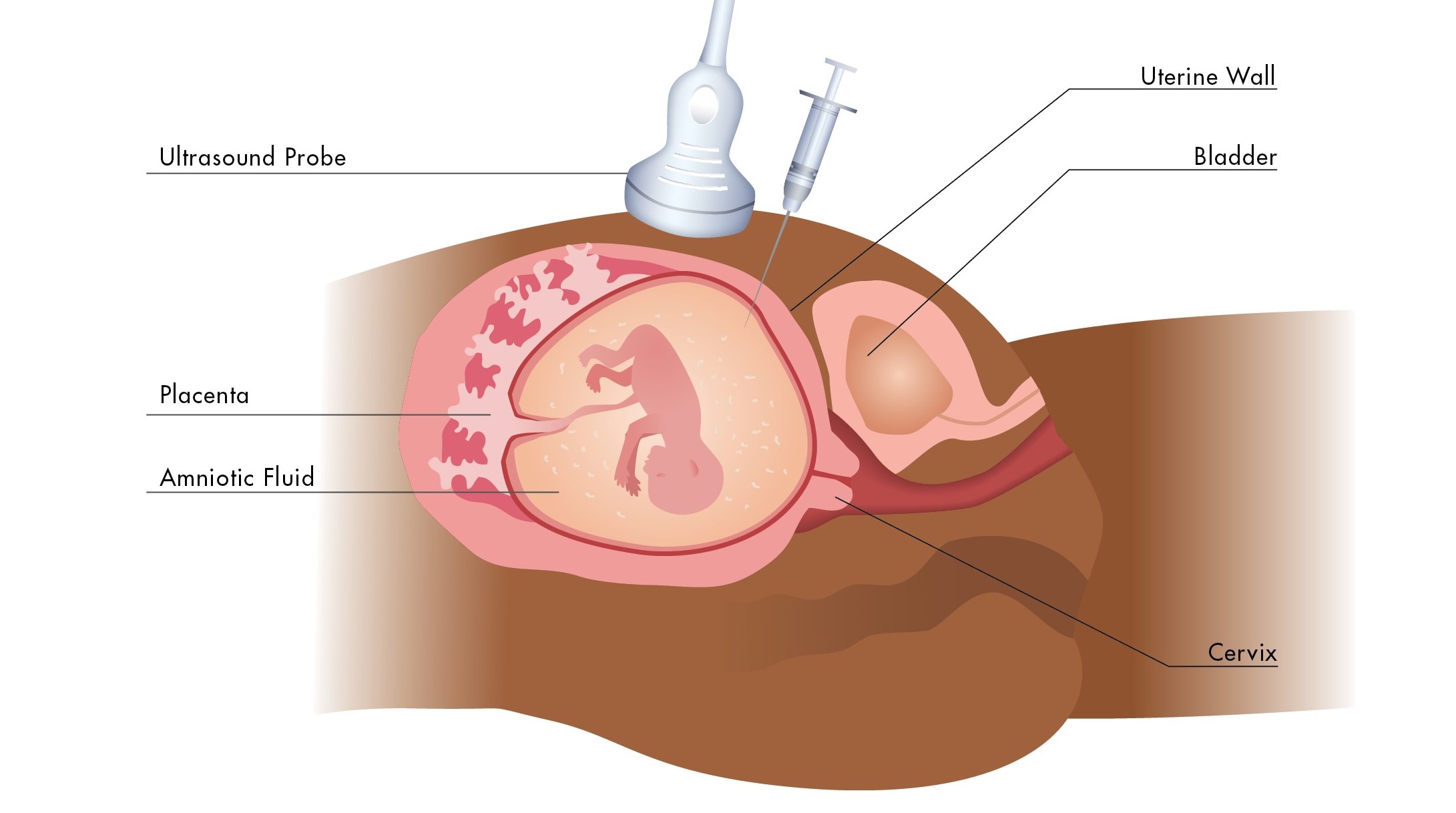
Illustration adapted from Genetic Counseling Aids, 7th Edition, Copyright 2020, permission for use granted by Greenwood Genetic Center
What to expect after amniocentesis
There is a risk of miscarriage from amniocentesis which can make it difficult to decide whether to have this procedure. It is important to remember that there is always a chance of pregnancy loss even if amniocentesis is not done. Amniocentesis increases this risk by less than 1%. Amniocentesis does not cause other problems for the baby (such as birth defects).
In some cases, amniocentesis is done later in pregnancy, in the third trimester. When amniocentesis is done later in pregnancy, there is a chance for going into labour earlier than expected. Premature babies, especially those born very early, often have complicated medical problems. The earlier your baby is born, the higher the risk of complications.
Results
The type of results that you get depends on which centre did the amniocentesis and the reason for testing. It is important to speak with your genetics specialist about what results you will get. All results are sent directly to your genetics specialist.
Rapid testing (also called QF-PCR)
Typically, you will get some results 2 to 4 days after the amniocentesis. These results can tell you if the baby has one of the following chromosome differences: trisomy 21, trisomy 18 or trisomy 13 or a sex chromosome difference.
Microarray testing
Depending on the hospital and the reason for testing, there might be a microarray test done from the same sample of fluid. Microarray testing can tell you whether there is material from other chromosomes that is extra or missing. These chromosome differences usually happen by chance in the sperm or the egg that made the baby. You get results from the microarray test in about 2 to 3 weeks.
| Video on Chromosomal Microarray Testing |
| A short video created by Alberta Health Services explains the microarray test and possible results. In this video, the testing was done through a blood draw. The way the test works and type of results are the same when the microarray is done through amniocentesis. |
Other genetic testing
Other genetic conditions can be tested in certain situations. Speak to your genetics specialist about whether there will be any other testing.
Benefits
The main benefits of amniocentesis are:
| Diagnostic |
| Amniocentesis can give a “yes” or “no” answer about chromosome differences. |
| Most accurate diagnostic test |
| Amniocentesis tests the DNA/genetic material from the baby directly which makes this the most accurate diagnostic test. |
| More conditions are tested |
| Amniocentesis can test for more genetic conditions compared to prenatal screening tests, including NIPT. |
| Quick results |
| You get information about trisomy 21, trisomy 18, and trisomy 13 faster than through prenatal screening tests. |
Limitations
The main limitations of amniocentesis are:
| Done later in pregnancy |
| Amniocentesis is done later in pregnancy compared to the other diagnostic test (CVS), so the results are also available later. |
| Cannot test for everything |
| Like any test, amniocentesis cannot look for every possible genetic condition. Amniocentesis will also not give you information about birth defects. Ultrasounds are still recommended to look at the growth and development of the baby. |
| There is a possibility to get results that are difficult to interpret |
| Rarely, we get results from amniocentesis that are difficult to interpret. This means that a genetic difference was found but we do not know what it means for the baby. Not every genetic difference has an impact on the baby's health and development. |

 Subscribe to this page
Subscribe to this page